7 UX Designer Portfolio Examples: A Beginner's Guide
Get inspiration for your entry-level UX portfolio with real world examples.
![[Featured image] A smiling person in a black shirt and necklace sits at their laptop and works on their UX portfolio in a brightly lit office.](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/1vchrSQ853YbMXncBSBwkr/48c1aa08827e27f61792e4bfa6077bca/UX_design_portfolio.png?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
How do you build a UX design portfolio with no experience? This is a common challenge for UX designers looking for their first paying job. By being strategic, however, you can still craft a stellar portfolio that shows off your skills before you land a job or client.
In this article, we’ll walk through seven types of portfolio case studies you can add to your portfolio that don't require you to have experience. We’ll also look at how working UX designers present these types of case studies in their portfolios and offer some takeaways and tips for making your portfolio shine.
To get started, let's look at some general guidelines and best practices for your UX design portfolio.
UX design portfolio examples
These seven types of UX case studies make excellent portfolio material for UX designers looking to get their start in the industry. Use these to build your portfolio, even if you've never completed UX design work for a paying client or employer.
1. The course assignment
Sometimes, the first project to go into your portfolio will be a UX project you worked on as part of a design course, UX boot camp, or degree program. These types of projects often simulate real-world situations by giving you the constraints of a brief to work from, as well as teammates to collaborate with.
Including a course assignment or capstone project in your portfolio can demonstrate your ability to:
Work with the constraints and challenges of a brief
Design on a fixed timeline
Collaborate with a team
Incorporate feedback into design iterations
Portfolio example: Phyllis Liu - Autonomous Ridesharing

Phyllis Liu, a Seattle-based UX designer who has worked for Facebook and Shopify, designed an autonomous car ridesharing experience as part of a project for a course at the University of Washington. In her case study, Phyllis is upfront about the constraints of the project, as well as what her team chose to focus on and why.
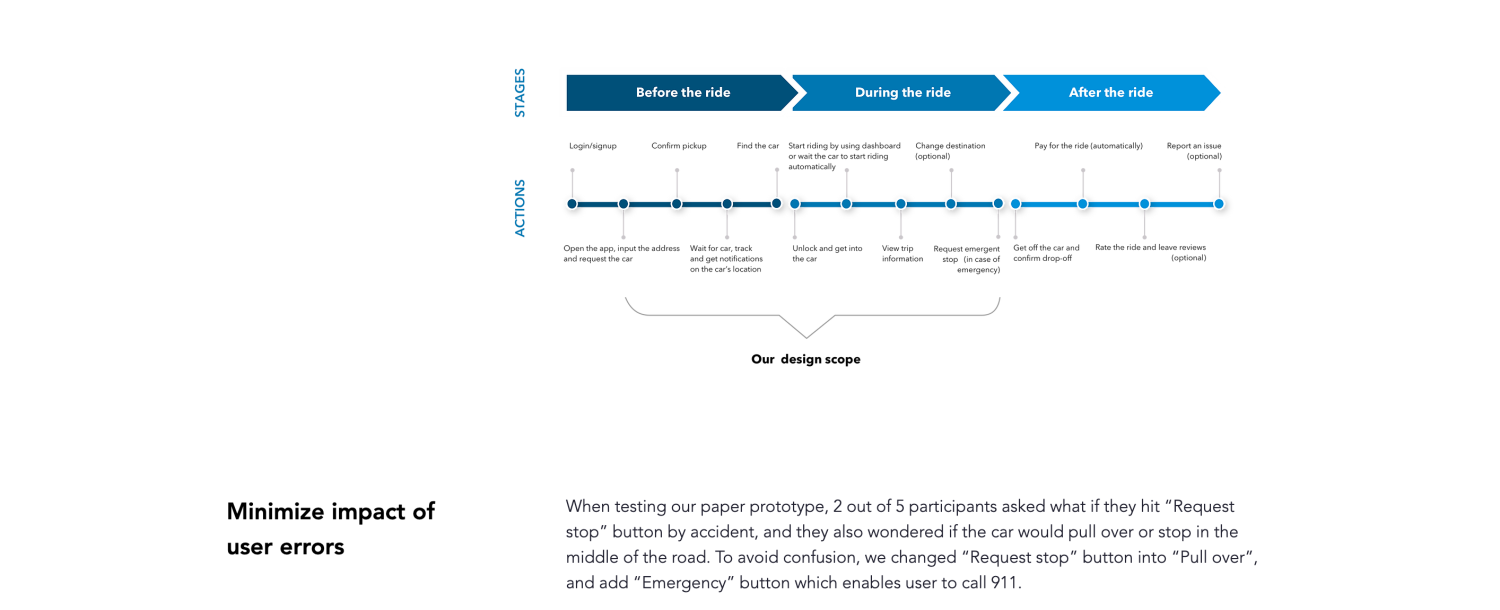
Scope of work chart for the Autonomous Ridesharing case study
For example, the team decided to focus their efforts on solving two specific user pain points—namely, finding the car and starting the ride without a driver. The case study walks through the project’s user research, product design iterations, validation through user testing, and user journey map before wrapping up with key takeaways and lessons learned.
Best practices:
Outline your role in the project and who else contributed. Mention what tasks you worked on.
Be clear about the scope and limitations of your project. What isn’t in the design, and why? Include a section outlining next steps if you were to continue the work.
Choose student projects with realistic constraints and real business value. Acknowledge any unrealistic elements in your case study.
Upon completion of the Google UX Design Professional Certificate on Coursera, you’ll have three end-to-end projects for your portfolio: a mobile app, a responsive website, and a cross-platform experience. Follow the link to get started for free.

2. The unsolicited redesign
An unsolicited redesign (sometimes called an uninvited redesign) is an excellent way to show off your skills before you ever land your first job as a UX designer. Pick an app or website that you’re familiar with, and make it better through your design process.
An unsolicited redesign gives you the structure of an existing product to start with—including an established target user base—while allowing you to put your user experience skills to work. This type of project is great for:
Developing UX skills for new designers
Establishing familiarity with the design process
Building your first portfolio case study
Portfolio example: Shu Jiang - Houzz

Shu Jiang, a product designer at Google, includes an excellent example of an unsolicited redesign of the app Houzz in her portfolio. She starts by outlining the challenge she set for herself, then walks through the steps of her design process, with plenty of images to document her work.
She includes affinity maps, a user persona, a task-flow chart, and low-fidelity, high-fidelity, animated, and clickable prototypes. She even validates her design decisions by testing her clickable prototype with users.
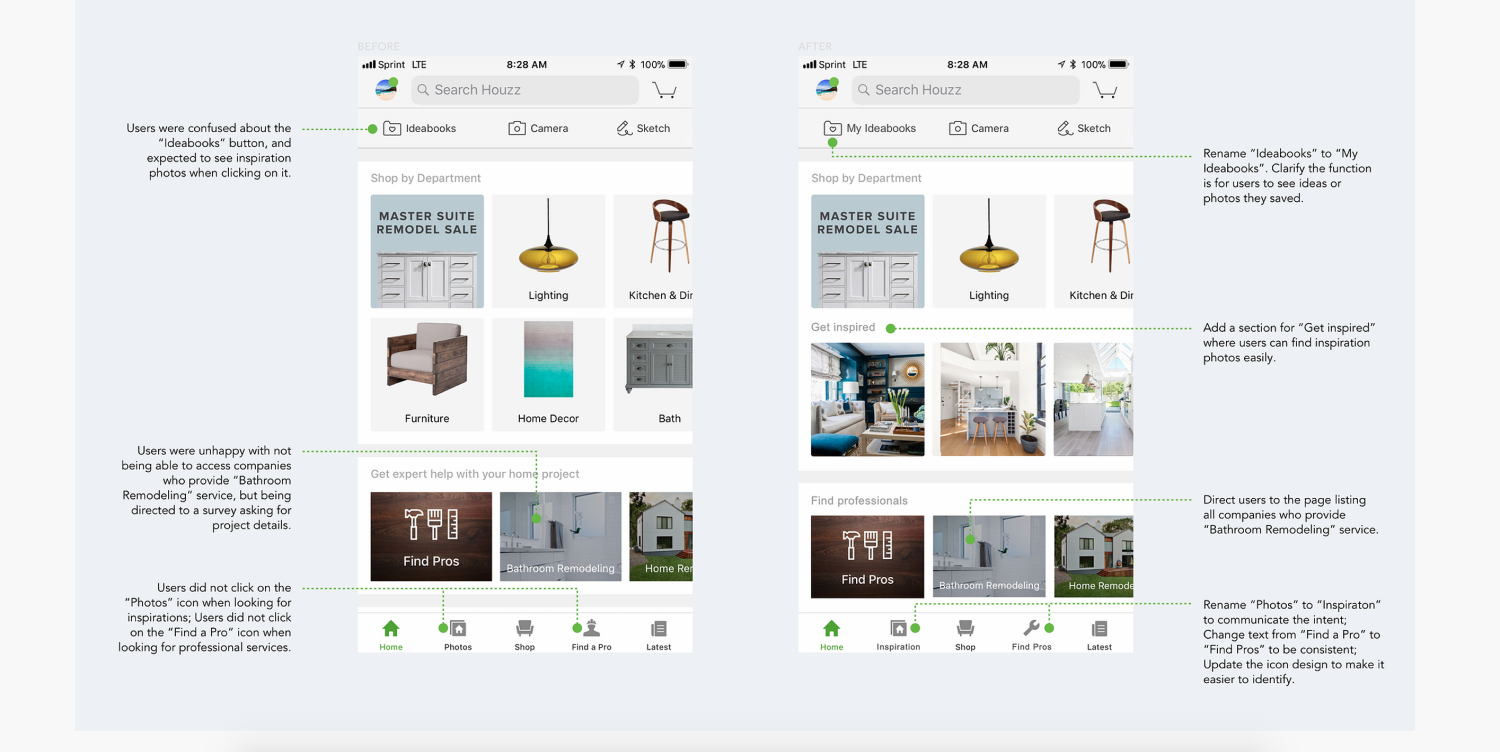
High-fidelity prototypes from an unsolicited redesign of Houzz
Best practices:
Clearly indicate that this is an unsolicited redesign and that you have no affiliation with the company.
Work through the entire process, including user research (your friends and family can be your first test subjects). Resist the urge to simply redesign the interface.
In your case study, be respectful of the original designers and avoid insulting their work. Focus on the advantages and benefits your redesign offers users.
3. The passion project
Another option for a case study you can complete without any formal UX design experience is to build a concept app or website from scratch. Think about a problem in your own life you wish had a solution to, or an app you’d love to have on your phone. Then design it.
This can be more challenging than an unsolicited redesign, as it lacks the inherent structure and constraints of an existing product. But it’s also an opportunity to let your creativity shine.
Portfolio example: Jeremy Stokes - Cultivate

Jeremy Stokes is a former Google UX intern and current product designer at Duolingo. His passion project, Cultivate, lays out a clear problem to solve: there’s a stigma around talking about mental health, particularly within the Black community. His solution? A service that uses plant care as a method to empower users to cultivate (and talk about) their own mental health.

User journey map from the Cultivate case study
Jeremy begins his case study by introducing the service, then takes you behind the scenes to see his design process. His case study includes his research methods, market analysis, detailed user persona, user journey map, and lots of early sketches and website iterations.
Jeremy also highlights his visual design strengths with a full brand guide that highlights the meaning behind his design choices (including typography, color palettes, logos, and visuals).
Best practice:
Focus on solving a real problem. Outline that problem and how you went about solving it in your case study.
You may not have a huge budget (or any budget at all) when working on a passion project. Be sure to mention what you would have done differently if you did.
Choose a project you care about. It’ll make the time and effort you put into it much more worthwhile.
4. The hackathon
During a hackathon, a group of designers and programmers get together to collaborate on a project. The idea is to have a functioning piece of software by the end of the competitive event, usually constrained to 24 to 72 hours.
Attending a hackathon allows you to design a real app while collaborating with a real team of other designers, developers, and engineers. A hackathon project in your portfolio can demonstrate that you can:
Think critically and solve problems under pressure
Be a team player
Prioritize important features and tasks

Yang Qian, a product designer at Palantir Technologies, presents a case study from a three-day LinkedIn hackathon for design and engineering students. Her team’s challenge was to design an app to help college students better connect with their classmates. The result? Matchy.
Yang presents the challenge, team, project duration, her role, and the skills she used to get it done in a clear and easy-to-read format. This case study does an excellent job of laying out user research findings. Short videos present user task flows in a way that doesn’t rely on big blocks of text.
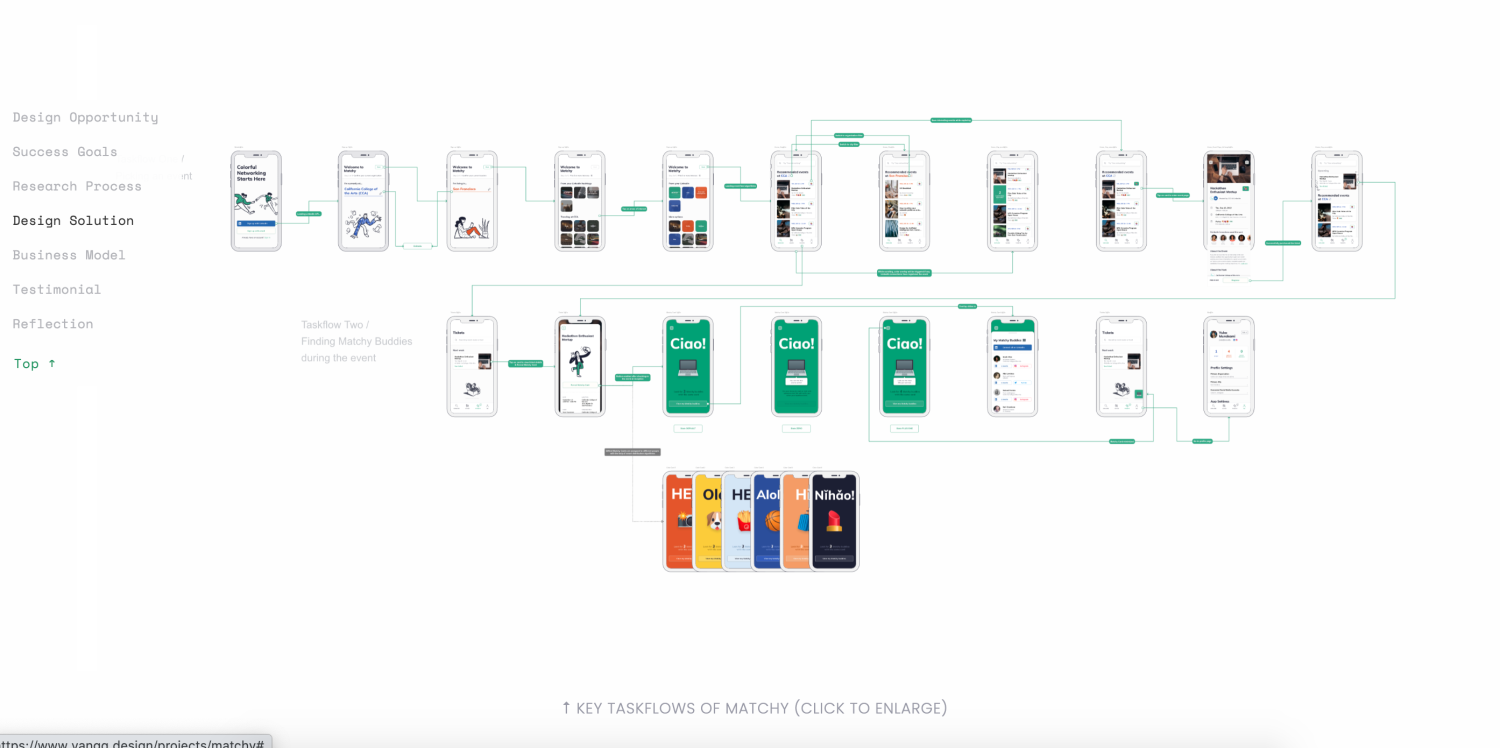
Taskflow chart for Matchy case study
After the event, Yang even added an illustration showing how the app would bridge the gap between user experience and business value based on feedback from hackathon judges.
Best practices:
Polish your hackathon project before presenting it as a case study (and acknowledge that you did so).
Focus on process over finished product. This is your opportunity to show hiring managers how you think under pressure.
Include any positive feedback from the judges, even if your project didn’t ultimately win.
5. The volunteer project
Another way to add real client work to your UX portfolio is to complete one or two small projects pro bono. Perhaps there’s a non-profit organization, school, or small business in your community that could use a website or app redesign.
Keep in mind that many nonprofits and small businesses may need more than just design. They may also need help with development and implementation (and the resources that go with it). In these cases, consider volunteering as a team or doing pro bono work as part of a nonprofit hackathon.
Portfolio example: Clayton Hopkins - #DullesJustice

Clayton Hopkins includes a few pro bono case studies in his portfolio in the form of Medium articles. A particularly interesting example is the website design he did for a group of lawyers offering free legal aid to travelers at Dulles Airport in response to the Muslim travel ban in 2017.

Homepage concepts for #DullesJustice project
In addition to walking through the entire UX design process step by step, Clayton offers insights into how he and his team responded to the urgency of the process, lessons learned along the way, and the results: three days after launch, the number of volunteers had increased from 100 to 1,200.
Best practices:
Choose projects that are fun or interesting to you and that you’d be proud to display in your portfolio.
Avoid signing a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) for unpaid work.
At the end of the project, ask for a letter of recommendation for future jobs.
One way to build your user experience portfolio: Volunteer
Looking for a way to volunteer your UX design skills? Check out these sites for opportunities:
•Get matched with a nonprofit project on Catchafire.
•Join a Code for America brigade to help design new tools for local communities.
•Lend your graphic design skills to a worthy cause with donate:code.

6. The UX design internship
Sometimes the path toward becoming a UX designer starts with an internship. Companies like Apple, Meta, Google, Amazon, and Airbnb are known to hire interns on their UX teams. You’ll find plenty of benefits to working as an intern—even if you’re unpaid—including:
Mentorship from experienced UX designers
Real-world experience
Behind-the-scenes industry insight
Networking opportunities
Projects for your portfolio
Best practices:
If you have to sign an NDA, make your case study password-protected or keep it general, focusing on the early ideation.
Tie your project to business results if possible.
Include a positive testimonial from your manager, supervisor, or peers from your time at the company.
7. The interview design challenge
You’ve landed your first interview for a UX designer role. But that doesn’t mean you can’t keep working on your portfolio. Many interviews include a design challenge—an interactive test meant to show how you think. With a bit of iteration and polish after the fact, you can transform these challenges (especially the take-home ones) into fresh material for your portfolio.
Portfolio example: Tammy Taabassum - Wish Design Challenge

During an interview with the e-commerce platform Wish, Tammy Taabassum completed a four-day design challenge where she was asked to improve the app in some way. Her project got her an internship, as well as a stellar portfolio piece.

Usability testing results chart for a Wish design challenge
Tammy presents her case study as a slide deck that lays out the challenge and the four steps of her design process. She digs into the insights and challenges uncovered during her user research, points back to other apps where she found inspiration and ideas, redefines the Wish app’s information architecture, and validates her design with usability testing. She also discusses how she would test and iterate with more resources, giving her interviewers a preview of the value she’d bring to the company.
Best practices:
If you received feedback during your challenge, include it in your case study. Show how you incorporated it into your design.
Be sure to take photos of your work when completing a whiteboard challenge during an interview.
Make clear that this was a design challenge so recruiters are aware of the limitations, such as time constraints.
UX design portfolio case study prompts
Here are a few additional prompts you can follow to generate new case studies for your portfolio:
Voice User Interface (VUI) Design:
Present a case study focused on designing a voice user interface for a digital assistant, smart speaker, or other voice-enabled devices, showcasing your ability to create intuitive and conversational interactions.
To start, describe the target users for the VUI, the scenarios in which it would be used, and the design considerations unique to voice interactions, such as natural language processing and speech recognition.
Accessibility Improvement:
Present a case study addressing accessibility challenges to make a digital product more inclusive and usable for users with disabilities, complying with accessibility standards and guidelines.
To start, describe the specific accessibility issues identified, the solutions implemented to address them, and the impact of these improvements on the overall accessibility and usability of the product.
E-commerce Experience Optimization:
Present a case study optimizing the user experience of an e-commerce platform, resulting in increased conversion rates, reduced cart abandonment, and an overall enhanced shopping experience.
To start, introduce the e-commerce platform and its significance within the context of the project. Provide background information on the challenges faced, such as high cart abandonment rates, low conversion rates, or usability issues identified through user feedback or analytics.

How to build a UX design portfolio
In most cases, your UX design portfolio should have three sections, a Home Page, an About page, and a collection of case studies (this page is often labeled Work).
Home
Your Home page should include a compelling headline introducing who you are and what you do. At minimum, your Home page should include a few sentences of text, an image, and a clear navigational menu. To make your Home page stand out, consider adding some of these elements:
Interactive design elements, such as sliders or carousels, which showcase your design skills
Case study highlights that include snippets from your top case studies, visually appealing images, and brief descriptions to encourage site visitors to learn more
Call-to-action buttons, placed strategically, asking site visitors to reach out to you or explore other pages of the portfolio
Testimonials from real users or people you've worked with to create the case studies
About
Your About page is the place to go into a bit more detail about who you are and how you got started in UX, especially if you’ve switched from another career. Here are some elements to add to make your About page stand out:
Details about why UX inspires you
Descriptions of projects you would like to complete or are currently working on
A list of UX skills you are building and classes you're taking
A description of your creative process, design approach, and how you like to work
Mentions of some of your favorite UX designers, influencers, or brands with great UX design
Did you know that nearly every US industry has seen an increase in AI-related job postings?
Learn to apply AI in your field productively and responsibly by enrolling in Google’s UX Design Professional Certificate.

Work
Early on in your UX journey, you may not have completed many design projects to include in your portfolio. But as you take classes, participate in hackathons, and work through passion projects, your collection of materials will start to grow.
While there’s no hard and fast rule about the number of projects to include in your portfolio, consider featuring three to five in-depth case studies. These should be your best work, and you can always swap them out for new case studies as you gain experience.
For each, consider including:
Project context, scope, and timeline
Your role and list of collaborators
Problem you set out to solve
Method or hypothesis for solving the problem
Primary and secondary research
User research and findings
User persona and user journey map
Design iterations (sketches, wireframes, low and high-fidelity prototypes)
Final product
Conclusion and metrics of success
Lessons learned
Optional sections
Depending on your amount of experience and personal preferences, you may also choose to include the following pages:
Resume: Give it its own page on the site, or if it's housed elsewhere, such as on your LinkedIn profile, provide a link to it.
Side projects or other work: If you have case studies or graphic design work beyond your few highlighted projects, give them a separate section where those who would like to see more can find them.
Contact: This doesn’t have to be its own page, but be sure to give potential employers or clients a way to get in touch after they've seen your work. Many portfolio and website platforms allow you to add a contact form to any page of your site so that site visitors can input their name, email, and a short message to get in touch.
UX portfolios: Choosing a platform
Having your own hosted website can often be worth the investment. But if you’d like to get started building a portfolio for free, these platforms can help you showcase your work:
1. Behance offers a free online portfolio platform for creative work, including UI, UX, and graphic design.
2. Dribbble, another popular UX portfolio platform, lets you share screenshots of your sketches, prototypes, and design concepts.
3. Adobe Portfolio is free with most Adobe Creative Cloud plans and allows you to create a customized site that synchronizes with Behance.
4. UXFolio starts free and allows you to build your professional-looking portfolio fast.

How do I make my UX designer portfolio stand out?
Now that we’ve reviewed the must-have sections of a UX portfolio and some examples of effective case studies, let’s examine some additional tips and best practices for building your portfolio.
For each case study, showcase your design thinking process, not just the finished product. Don’t skip steps.
Document your process and include visuals in your case studies. Show your design process in action through photos, sketches, and screenshots.
Use emotive language to show empathy. This is particularly important when giving background on the user satisfaction goal you set out to achieve.
Tie great UX back to business value. How does solving a user problem positively impact the business?
Highlight your specialty. If you aim to be a generalist, choose projects where you worked on all elements of the design process. If you’re more interested in user research or user interface (UI) design, prioritize these elements in your case studies.
Make sure your portfolio provides a good UX. Your portfolio website is itself a demonstration of your skills in leading site visitors through a logical and engaging experience.
Choose color schemes, fonts, images, and other visual elements that represent your design preferences and personal brand. For example, maybe you choose a minimalist design because you like a clean, uncluttered look. Or, maybe you choose bold colors and vibrant patterns to reflect your dynamic personality.
Put effort into composing content that is engaging and informative.
Try to include at least one live case study. Some work may need to be password-protected due to NDAs, but you want to give recruiters something to look at without having to email you for a password first.
How to enhance your UX designer portfolio
If you still need projects to fill the gaps in your portfolio, you have plenty of options. The list below outlines a few 100-percent online, self-paced programs that you can use to expand your UX design skills, bulk up your portfolio, and support your UX career.
Google UX Design Professional Certificate: In addition to earning a Professional Certificate from an industry leader, this online course can be used to add three different end-to-end projects to your portfolio:
A mobile application
A responsive website
A cross-platform experience
Meta Front-End Developer Professional Certificate: Throughout this program, you'll manage a project in GitHub using version control, Git repositories, and the Linux terminal. You'll also have the opportunity to participate in a Capstone project to build the front end of a web application. By the end, you'll have completed nine projects in a lab environment or web application and earned a Professional Certificate from Meta.
Build your UX design portfolio today
Take the next step in your UX design career by creating projects you can add to your portfolio. Coursera offers top-rated courses and Specializations to help you achieve your career goals:
To design an app for your portfolio, take our Guided Project, Design a mobile app interface with Moqups. You'll create a flow and wireframes for all the app's stages and then transform those wireframes into mockups that you can add to your UX portfolio.
To get a crash course in web design, take CalArts' Web Design: Wireframes to Prototypes. With this 27-hour five-module course, you'll apply UX research to actual user interfaces by creating wireframes, high-fidelity mockups, and clickable prototypes. The course is a continuation of UI / UX Design Specialization, so if you also need skills in research, planning, and content design, you can develop a complex website by taking the two courses together.
To gain foundational UX design skills, take Google's UX Design Professional Certificate. This popular series of courses is designed to get you ready for an entry-level UX design role in as little as four weeks.
Coursera Staff
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.